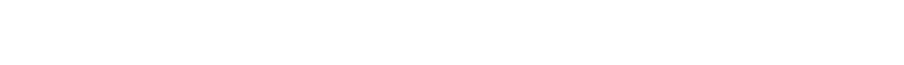Hermetic Wiper – Targeted destructive malware
Summary
On February 24, 2022, we saw one of the largest targeted attacks in history that focused solely on the destruction of critical information and resources. This attack employed the use of a new type of destructive malware that began executing against Ukrainian targets shortly before Russia’s physical military invasion of the country.
The malware used in this attack has been coined HermeticWiper, as the binaries are signed using a certificate by Hermetica Digital Ltd. This malware leverages legitimate EaseUS Partition Master drivers to access the disk of the victim’s computer, which in turn targets the Master Boot Record (MBR) of the disk. The MBR holds critical partition data necessary for computer systems to boot into an operating system. By targeting the MBR, the malware can carry out its intended goal of causing the data on disk to be destroyed, which would then be difficult and time-consuming to recover. VMware Carbon Black’s Global Incident Response Threat Report highlighted the steep 51% increase in the use of destructive malware in targeted attacks.
Initial evidence suggests that these attacks are highly targeted and have been in development for some time as the original executables were compiled on December 28, 2021. Newer samples from February 23, 2022, have recently emerged which highlights this adversary’s ability to adapt and evolve quickly to execute their goal.
During execution, the attacker first targets privilege escalation before targeting the Domain Controller. Once access to the Domain Controller is achieved, the attacker will utilize Active Directory to move laterally to deploy and execute the malware on additional systems. The Domain Controller itself is left intact to allow for widespread malware distribution within the victim network.
There have been reported instances of ransomware being deployed concurrently with the wiper, dropping a ransom note on the system. The ransomware is then utilized to drop and execute the wiper in the environment.
Technical Analysis
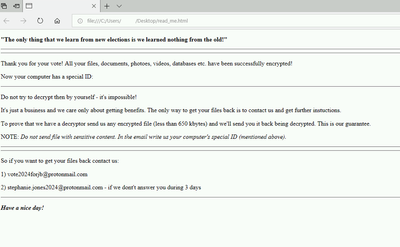
Upon execution, the HermeticWiper binary drops a driver file in the folder C:\windows\system32\drivers\*.sys. This file is an EaseUS Partition Master driver which is leveraged to access disk partitions for destructive purposes. Additional drivers, embedded in the resources section of the binary are also decompressed using the Windows LZ32.dll, an extraction library, depending on the operating system version. The drivers used include:
- DRV_X64/DRV_XP_X64
- DRV_X86/DRV_XP_X86
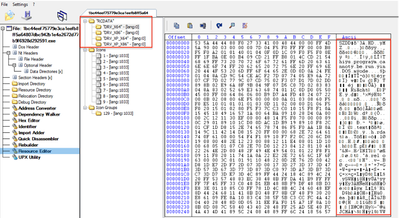

Once the driver is installed, the registry subkey HKLM\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\CrashControl is modified, setting the value of the key “CrashDumpEnabled” to 0, disabling the creation of local crash dumps. The driver is registered as EPMNTDRV, allowing the malware to interact with the local drives attached to the system. The malware attempts to overwrite the first 512 bytes, which is the location of the MBR of the bootable drive.


The currently known HermeticWiper samples are detected and blocked by the Endpoint Standard product by default when using the Standard policy. The Enterprise EDR product will detect current samples by default. We recommend ensuring that you are using the most current VMware Carbon Black Cloud sensor version.
It is critical that comprehensive and robust data backup protocols and solutions are in place which meet the 3-2-1 data backup rule to ensure data restoration is possible during a worst-case scenario, and to protect against the advanced capabilities of this adversary. We strongly urge customers to have redundant methods for data storage with at least one backup available offline, which will help with the recovery process in the event of successful encryption or destruction.
Indicators of Compromise
| Indicator | Type | Context |
| 0385eeab00e946a302b24a91dea4187c1210597b8e17cd9e2230450f5ece21da | SHA256 | HermeticWiper |
| 1bc44eef75779e3ca1eefb8ff5a64807dbc942b1e4a2672d77b9f6928d292591 | SHA256 | HermeticWiper |
| 2c10b2ec0b995b88c27d141d6f7b14d6b8177c52818687e4ff8e6ecf53adf5bf | SHA256 | HermeticWiper |
| 3c557727953a8f6b4788984464fb77741b821991acbf5e746aebdd02615b1767 | SHA256 | HermeticWiper |
| 4dc13bb83a16d4ff9865a51b3e4d24112327c526c1392e14d56f20d6f4eaf382 | SHA256 | Ransomware |